- Shanghai Zhongshen International Trade Co., Ltd. - Two decades of trade agency expertise.
- Service Hotline: 139 1787 2118
Export trade has become an important bridge connecting the economies of different countries. However, every cross - border transaction is accompanied by risks of varying degrees. Especially for small, medium - sized and micro enterprises, how to assess and manage these risks has become the key to their successful going global. Among many export destinations, what kind of signal does the risk index of Malaysia show?
什么是SMERI?
SMERI (Small and Medium Enterprises Risk Index), that is, the Small and Medium - sized Enterprise Risk Index, is an indicator specifically designed to assess the risk level faced by small and medium - sized enterprises (SMEs). This index usually takes into account various factors, including market environment, financial situation, industry characteristics, policy changes, credit availability, and other external and internal factors that may affect the operation and growth of SMEs. The purpose of SMERI is to provide investors, lending institutions, government departments, and entrepreneurs with a quantitative tool to evaluate the risks and stability of SMEs operations.
Theoretically, the lower the SMERI index, the smaller the risks faced by enterprises. Correspondingly, the business environment and future development prospects of enterprises are considered to be more stable and secure. Therefore, from the perspective of risk management and investment safety, a lower SMERI index is usually regarded as more favorable.
According to the latest report of SMERI, Malaysia, as an important trading partner of Chinese small, medium - sized and micro enterprises, has its overall credit risk level rated as low. This is undoubtedly a positive signal for enterprises that are considering or have already carried out business in the Malaysian market. However, in order to understand the specific situation behind this assessment more deeply, we need to conduct a detailed discussion from the following aspects.

一、SMERI指数得分情况
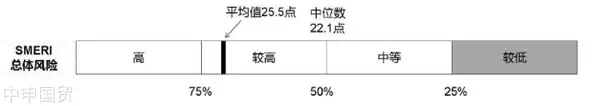
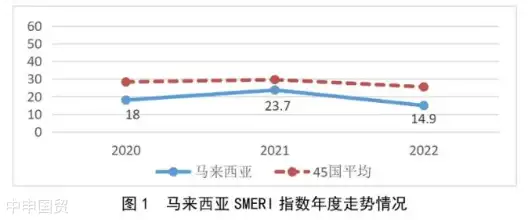
马来西亚的SMERI指数为14.9点,这一分数低于报告所涉及的45个国家的平均水平10.6个点,表明与马来西亚企业交易的总体信用风险较低。这一结果部分得益于马来西亚政府近年来在稳定经济、促进内需以及优化贸易环境方面所做的努力。然而,马来西亚SMERI指数的波动下降趋势也提示着市场存在不确定性,需要企业进行持续的风险评估和管理。
II. Macroeconomic Indicators
Malaysia scored 16.7 points on macroeconomic indicators, far lower than the average, reflecting that its macro - economic risk level is low. In 2022, Malaysias economic growth rate reached a 22 - year high, showing a strong recovery momentum. This benefits from a series of economic stimulus measures taken by the government, such as consumer subsidies and social welfare programs, as well as the growth of the service and manufacturing industries. This indicator shows that from a macro - economic perspective, the Malaysian market provides a relatively stable and favorable trading environment for Chinese small, medium - sized and micro enterprises.
III. Trade Environment Indicators
On trade environment indicators, Malaysia scored 22 points, also lower than the average, indicating that its trade environment risk towards China is low. This result reflects the increase in Malaysias import demand for Chinese goods and services, as well as the stable standardization of trade regulations. With the possible reduction of tariff levels and the weakening of anti - dumping and counter - subsidy measures, Malaysia will be a more open and friendly trading partner for Chinese enterprises.
IV. Subject Quality Indicators
The subject quality indicators of Malaysian enterprises scored 11.0 points, far lower than the average of 23.5 points, reflecting that the credit status of Malaysian enterprises is good, with a low risk level. This means that Malaysian buyer enterprises generally have a high credit quality, providing stable partners for Chinese small, medium - sized and micro enterprises.
V. Payment Status Indicators
Malaysian enterprises trading with Chinese small, medium - sized and microforeign tradeenterprises scored 13.9 points on payment status indicators, 1.3 points higher than the average level, indicating that the payment credit risk of Malaysian buyer enterprises is high. This reminds Chinese exporters to strengthen the review and monitoring of the buyers payment ability when conducting transactions with Malaysian enterprises.
VI. Attention to Export Destinations
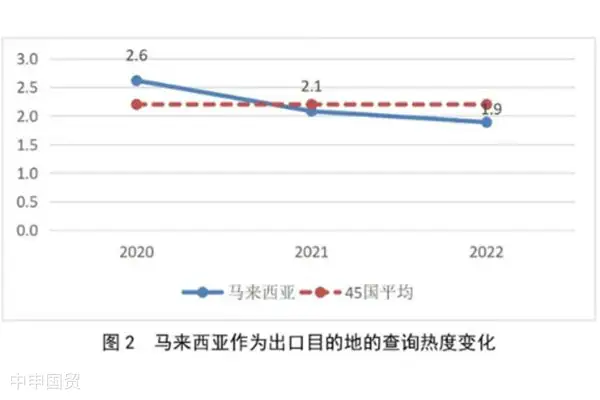
Data from Sinosure shows that the comprehensive query popularity of Chinese small, medium - sized and micro enterprises for Malaysia has been declining year by year, and is generally lower than the average level of 45 countries. This may reflect that Chinese enterprises attention to the Malaysian market has weakened, or due to the improvement of market risk awareness, enterprises are more cautious in choosing export destinations.
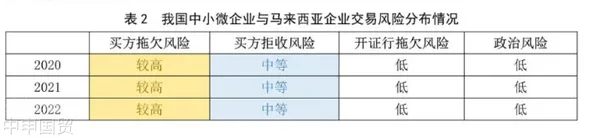
VII. Distribution of Loss Reasons
According to the business data of Sinosure, the main reasons and risk distribution of export losses of Chinese small, medium - sized and micro enterprises to Malaysia show that payment default is one of the main risks. This further emphasizes the importance of strengthening the assessment of the payment ability and credit status of Malaysian buyers.
Based on the above analysis, the Malaysian market presents a low risk and good development potential for Chinese small, medium - sized and micro foreign - trade enterprises. Although there is uncertainty in the global economic environment, Malaysia has a good macro - economic foundation. Coupled with the governments active measures to promote economic recovery and optimize the trade environment, it provides a stable export destination for Chinese small, medium - sized and micro enterprises. However, when making decisions to export to the Malaysian market, enterprises still need to pay attention to market dynamics and strengthen risk management to cope with possible market fluctuations and challenges.
Related Recommendations
Knowledge Base
Contact Us
Email: service@sh-zhongshen.com
Related Recommendations
Contact via WeChat

© 2025. All Rights Reserved.沪ICP备2023007705号-2 PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912
PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912








